As our population ages, the prevalence of chronic illnesses rises, with respiratory ailments including Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and asthma becoming more common among the elderly. These illnesses not only reduce quality of life, but also place a tremendous strain on healthcare systems. This blog post examines the effects of chronic respiratory disorders on the elderly, concentrating on symptoms, management options, and measures to improve daily life.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD)
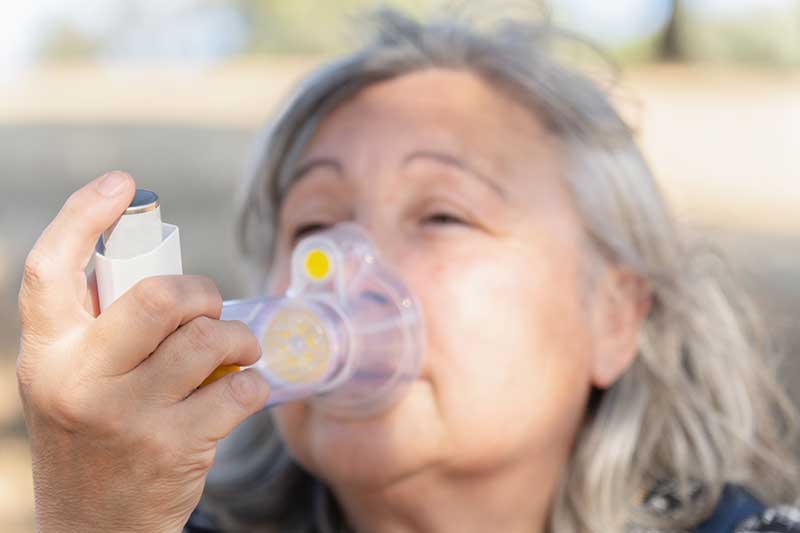
COPD is a set of progressive lung illnesses, the most prevalent being emphysema and chronic bronchitis. This condition is characterized by an increase in breathlessness. Many people mistake the early signs of COPD for normal aging or a lack of fitness, yet detecting COPD early can lead to improved treatment.
Symptoms of COPD
- A persistent cough with mucous
- Shortness of breath, especially during strenuous activity.
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness.
Managing COPD
COPD is mostly caused by prolonged exposure to irritants that harm the lungs and airways. In wealthy countries, tobacco smoke is the most common culprit. Air pollution, occupational dust, and chemicals all contribute to the condition.
COPD management includes medicines, respiratory rehabilitation, and supplementary oxygen for severe patients. Lifestyle adjustments like stopping smoking and avoiding lung irritants are also important. Pulmonary rehabilitation, which combines exercise, education, and support, can dramatically enhance one’s quality of life.
Asthma among the elderly
Asthma is commonly associated with childhood, however it can affect people of any age. Asthma presents special challenges in the elderly due to aging-related physiological changes and the presence of other chronic disorders.
- Symptoms of asthma.
- Shortness of breath.
- Chest tightness or pain.
- Shortness of breath causes trouble sleeping.
Exhaling produces a whistling or gasping sound.
Asthma in the elderly may go undiagnosed since it is assumed that shortness of breath is a typical component of aging. Furthermore, other frequent illnesses in the elderly, such as heart disease, might obscure or complicate asthma diagnosis and therapy.
Managing Asthma
To manage asthma, it’s important to identify triggers, evaluate symptoms regularly, and take drugs such inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting bronchodilators. Elderly patients should work with their healthcare physician to build an asthma action plan that is tailored to their specific requirements.
Living Well with Respiratory Diseases
Living with a chronic respiratory condition is difficult, particularly for seniors. Here are some strategies for improving your quality of life:
- Stay Active: Regular, moderate exercise can strengthen the muscles involved in breathing and increase overall physical stamina.
- Healthy Diet: A well-balanced diet promotes immune function and general health.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare practitioner can help monitor the progression of the disease and alter therapy as needed.
- Educate yourself and communicate. Understanding your health and freely communicating your symptoms with your doctor might lead to more effective disease management.
While COPD and asthma are serious health concerns for the elderly, understanding these conditions and implementing appropriate management measures can result in a significant improvement in quality of life. If you or a loved one are suffering respiratory problems, see a doctor for an evaluation and treatment plan.