Chronic problems are an unavoidable aspect of aging for many people, with diseases including hypertension, diabetes, arthritis, and heart disease becoming typical companions in later life. The treatment of these disorders in older persons requires a complex combination of medical care, lifestyle changes, and psychological support. This blog intends to educate caregivers and seniors with effective ways for navigating the hurdles of chronic disease management, thereby improving quality of life.
Understanding the Dynamics of Chronic Conditions in Elderly Adults
Aging causes a variety of physiological changes that might influence the progression and treatment of chronic diseases. Decreased mobility, diminished cognitive skills, and other age-related changes can complicate the care needed. Proactively addressing these concerns is critical for good chronic disease management.
Strategy 1: Comprehensive Care Planning
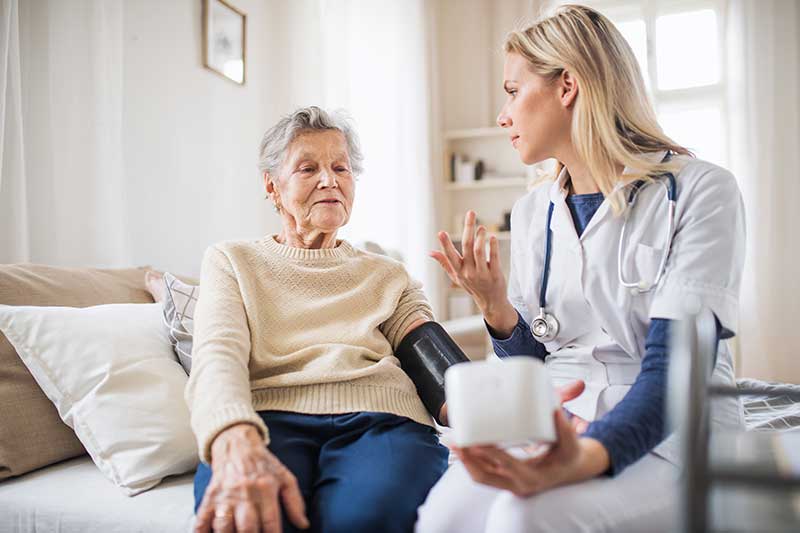
Personalized Care Plans: Each senior’s health situation is unique, and so should their treatment strategy. Healthcare practitioners should create treatment regimens that are tailored to individual health problems, lifestyle preferences, and social circumstances.
Interdisciplinary Approach: Effective management frequently necessitates a collaborative effort among doctors, nurses, nutritionists, physical therapists, and, in certain cases, mental health practitioners. This concerted effort guarantees that all areas of the patient’s health are addressed.
Strategy 2: Medication Management
Regular Medication Review: Medication regimes should evolve in tandem with changing bodies and situations. Regular consultations with a healthcare professional can help to avoid the hazards associated with polypharmacy—the use of many medications—which is common among senior persons.
Regimen Simplification: Aligning medication schedules with daily routines can help increase adherence and reduce confusion, which is especially essential for patients experiencing cognitive loss.
Strategy 3: Lifestyle modifications
Diet and nutrition: Proper diet is critical in controlling chronic conditions. Diets high in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help you lose weight and alleviate symptoms of conditions including diabetes and heart disease.
Physical Activity: Regular, light exercise tailored to the individual’s capacity can aid in mobility maintenance, pain relief, and overall well-being.
Strategy 4: Education and Empowerment
Self-management Education: Educating elders about their diseases and how to manage them can encourage them to take an active role in their treatment. Knowledge is a valuable instrument that can lead to better results.
Support Groups: Attending support groups can provide emotional support and practical help, lowering feelings of isolation and worry that are common with chronic illnesses.
Strategy 5: Technological Integration
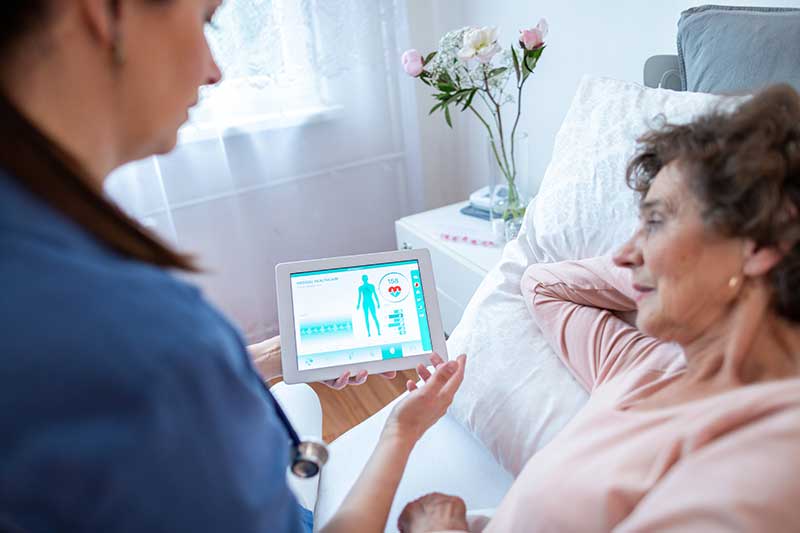
Use of Technology: Telehealth services and medical alert systems are examples of modern technology that can help manage chronic diseases. These instruments provide ease and a way of quick reaction in emergencies, which is especially useful for persons with limited mobility.
Strategy 6: Psychological Support
Mental Health Services: Chronic diseases can be both mentally and physically exhausting. Access to mental health professionals can help elders deal with frustrations and worries, thereby enhancing their general mental health and quality of life.
Managing chronic illnesses in older persons is a difficult endeavor that demands meticulous planning and organization. Caregivers and seniors can successfully address these difficulties by taking a holistic strategy that includes medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and psychological support. The goal is not just to control symptoms, but also to improve the quality of life for seniors, giving them not only more but better years.